
Research landscape
In Belgium, approximately 113,000 persons are employed in R&D, with more than 73,000 of these working as researchers (2015 figures). Nearly half of this total is to be found in the business sector. Intra-muros R&D Expenditure (R&D intensity) represents 2.47% of GDP, placing Belgium among the most active EU Member States.
For a full overview of the Belgian research landscape and of the Belgian science and technology indicators, please download the (Belgian Report on Science, Technology and Innovation (BRISTI)). It shows the complexity and the richness of the National IR&I landscape.
For up-to-date information on research and innovation in Belgium, please consult the webpages of BELSPO’s Scientific and Technical Information Service and innovationdata.be.
The Federal Science Policy Office (BELSPO) is is the federal administration in charge of science policy.
There are 10 Federal Scientific Institutions (Museums and Research Institutes) that fall under BELSPO:
- Institute for Cultural Heritage
- Institute of Natural Sciences
- Institute for Space Aeronomy
- Meteorological Institute
- Museums for Art and History
- Museum for Central Africa
- Museums of Fine Arts
- Observatory and Planetarium
- Royal Library
- State Archives (of which SOMA-CEGES is now a DG)
There are three other Federal Scientific Institutes that fall under other administrations:
- National Institute for Criminalistics and Criminology (in French or Dutch)
- Penitentiary Center for Research and Clinical Observation
- Sciensano (merger of the Scientific Institute of Public Health & the Veterinary and Agrochemical Research Centre)
Flanders, centre of innovation
The backbone of the Flanders’ knowledge sector is shaped by the 5 university associations, the 5 strategic research centres, and a number of other knowledge institutes in specific domains such as marine sciences, tropical health, agricultural research, and various collective research institutes active in specific fields. Several of these seats of knowledge in Flanders are recognized as centres of excellence in their field of activity and conduct research integrated in renowned international networks and with partners throughout the world. Some of these, such as KU Leuven, UGent, IMEC or VITO, have established subsidiary activities abroad (USA, Asia), often involving local counterparts or partners.
The main contributors in the research and innovation landscape are businesses and industries. Companies in Flanders (and Belgium) are among the most innovative in the EU: 62% of all industrial companies and service businesses conduct a form of innovation, according to the bi-annual Community Innovation Survey (CIS). In only 2 countries, Germany and the Grand-Duchy of Luxemburg, do companies innovate more than in Flanders (EU-27: 53%). Of all people employed in Flanders, 9.4% are active in an innovative sector. Flanders is specialised in labour intensive (plastics, diamonds) and capital intensive (vehicles) goods. The main high-tech export product is pharmaceuticals, that represented 61.3% of all high-tech exports in 2014.
Are you looking for research topics, research teams or researchers? If so, you'll find them on the Flanders Research Information Space. In addition, the expertise centre ECOOM maps the Flemish R&D and innovation landscape and will give you a good overview of the research landscape in Flanders.
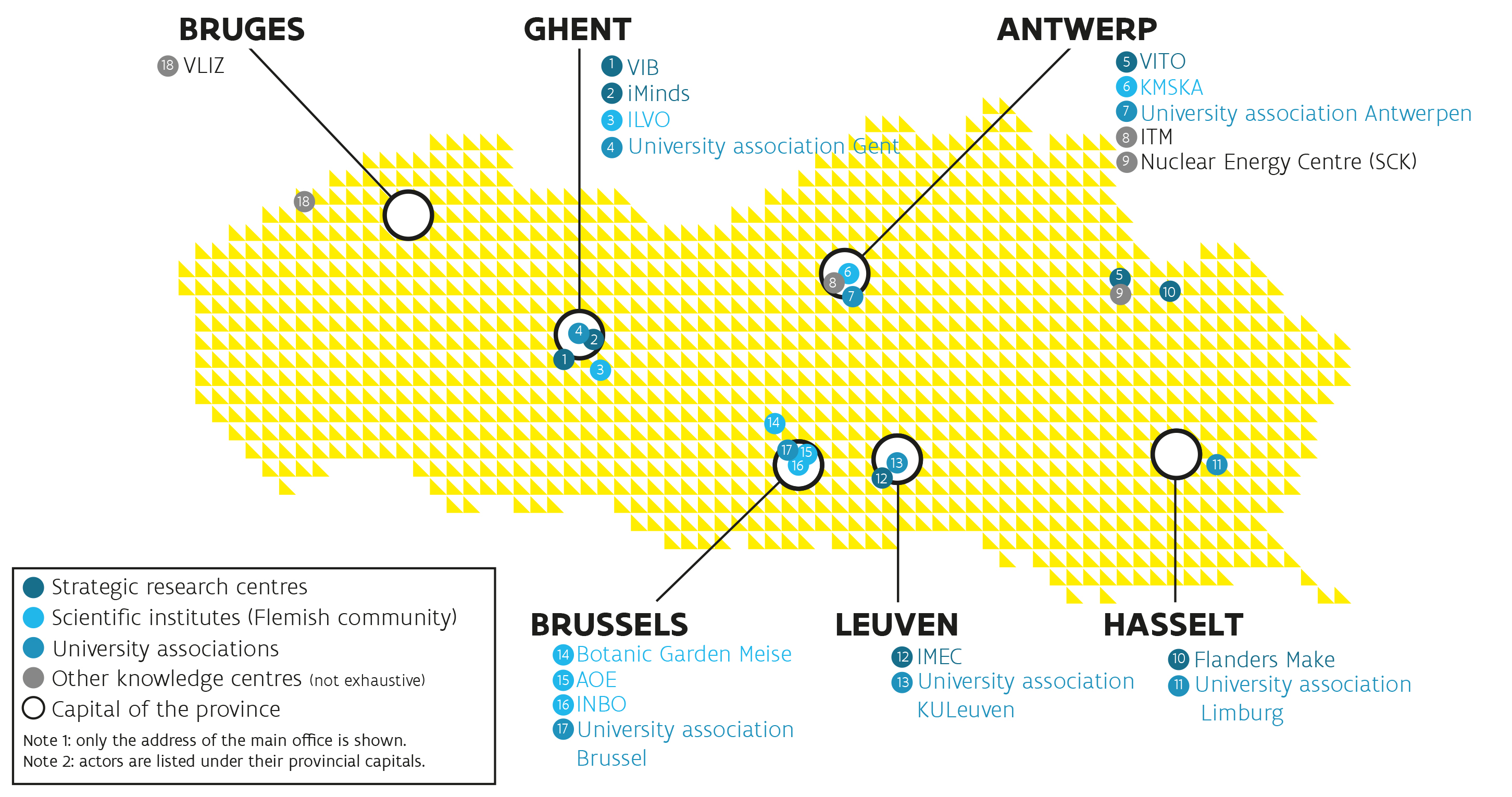
The following table presents a brief overview of the main (types) of institutes and players acting within the research and innovation system in Flanders:
Type of organization | Actors |
|---|---|
| Public authority: policy preparation, monitoring and evaluation | EWI Department |
| Public authority: policy execution (agencies) | AIO, FWO, PMV, (FIT) |
| Advisory council | VARIO |
| Strategic research centres | IMEC, VIB, VITO, Flanders Make |
| Scientific institutes (Flemish Community) | Agency Botanic Garden Meise, ILVO, INBO, KMSKA, AOE |
| University associations (one university with one or more higher education institutions) | Antwerpen, Brussel, Gent, KU Leuven, Limburg |
| Other knowledge institutes | ITM, VLIZ, Energyville, CMI, NERF, CRC, BioBase Europe |
| Spearhead clusters | Proposals being prepared for possible clusters in the fields of Materials, Sustainable Chemistry, Agro-Food, Logistics, Smart Energy (non-exhaustive listing) |
| Innovation platforms | FISCH, Flanders Drive, Flanders FOOD, Flanders Inshape, Flanders Synergy, MIX, SIM (including Flamac), VIL, VIM, MIP3.0, Social Innovation Factory |
| Technology transfer offices (TTO) from the 5 universities, and from the 5 strategic research centres | Universities: KU Leuven Research & Development, UGent Tech Transfer, Tech Transfer Office UHasselt, Interface AUHA, VUB Technology Transfer Interface |
| International institutes, organisations or platforms in the STI field, located in Flanders | Von Karmann Institute (Sint-Genesius-Rode), IOC for the IODE (Ostend), EMODnet (Ostend), EMB (Ostend), IRMM (Mol), UNU-CRIS (Bruges), ESA Business and Innovation Centre (Geel) |
| Science / technology parks | Greenbridge (Ostend), Evolis (Kortrijk), Ardoyen, Eiland Zwijnaarde (Ghent), Waterfront (Niel), Zellik (Asse), Arenberg, Haasrode (Leuven), Feed Food Health (Tienen), Thor Park (Genk), Research Campus Hasselt (Hasselt), Greenville (Houthalen-Helchteren) |
In the French-speaking Community, 5 universities play a key role as research performers: the Catholic University of Louvain (UCLouvain), the Free University of Brussels (ULB), the University of Liège (ULiège), the University of Mons (UMons), the University of Namur (UNamur), who participate in international university networks, whether institutional or disciplinary, and maintain numerous student exchange partnerships with universities all over the world. These university institutions, with their laboratories and research centres, enjoy access to cutting edge scientific support and top-quality infrastructure. More than 12,000 researchers are working in the French-speaking Community.
For more information about
- - Research career opportunities in French-speaking Belgium
- - F.R.S.-FNRS : https://www.frs-fnrs.be/en/
- - Universities : http://www.cref.be/;
Other useful links:
- - Official Portal of Scientific Research in Wallonia-Brussels Federation
- - WBI (the agency responsible for international relationships in the Wallonia-Brussels Federation)
- - LiEU Network (the Businesses and University Link)
- - SynHERA (the office which represents applied research within French-speaking Universities of Applied Sciences -UAS- and associated Research Centres)
